Artificial Intelligence (AI) is changing the game in digital design! Research indicates that:
- 62% of business professionals believe AI will have a significant impact on their industry in the next five years.
- 44% say they have already gained a competitive advantage from AI technologies.
- 78% of UX designers believe that AI will create new job opportunities in the field, while 64% think it will change the way they approach design tasks.
These stats are indicating the transformative potential of AI in enhancing user experiences and its importance in shaping the future of UX designers and UX researchers.
AI offers many chances to improve user interfaces and make design processes smoother than ever. However, it also brings some challenges that UX professionals need to handle. It’s all about enjoying the excitement of new ideas while making sure users stay happy and engaged. So, put on your creative hats and let’s explore this exciting AI design journey together!
Whether you’re a tech newbie, a business owner, or just someone interested in new technologies, this article will help you understand the basics of how AI and UX process work together.
I’m a UX researcher at Droids On Roids, a company that builds innovative digital products for a diverse range of clients. My job is to understand users’ needs and help create usable and effective products via user research. I use AI tools on a daily basis to gather and analyze user feedback, which helps us design better experiences. These AI powered tools not only save time but also provide deeper insights into what users truly want, connecting traditional user research methods and UX tools with AI-driven results. They challenge our assumptions, initiate meaningful discussions and guide strategic decisions, enhancing our ability to create products that resonate with users.
The evolution of AI in UX design
The journey of AI in UX design and research is an interesting one that started with the rise of digital technology and the need for more personalized and efficient user experiences. In the beginning, AI was like a curious experiment, as we were trying to figure out how machines could help create better designs and improve how users interact with them. It was a time when people were eager to explore how technology could make our digital experiences more intuitive.
One of the first significant steps in AI for UX design was the development of machine learning algorithms that could analyze large amounts of user data. These algorithms enabled designers and researchers to understand patterns in user behavior more accurately and consequently make data-driven decisions to enhance the usability of their products. For example, early AI tools could analyze how people navigated websites, helping designers identify users’ pain points and optimize the interface accordingly.
Another interesting aspect of AI’s early involvement in UX was in natural language processing (NLP), which enabled the creation of chatbots and virtual assistants. These tools were among the first AI-driven features that directly interacted with users, helping them perform tasks like finding information or troubleshooting issues without the need for human intervention. This marked a significant shift in how UX designers approached user interaction, as it introduced a new layer of personalization and automation.
As AI continued to evolve, it began playing a more substantial role in design automation. Tools like Adobe Sensei started to emerge, offering designers AI-powered suggestions for layouts, color schemes, and even content generation. This allowed designers to focus more on the creative aspects of their work while relying on AI to handle repetitive tasks and provide data-backed design options.
AI’s beginnings in UX design and research were rooted in the need to make digital products more user-friendly and efficient. Through advancements in data analysis, natural language processing, and design automation, AI gradually became an indispensable tool for UX professionals, transforming how we design and interact with digital products today.
The challenges and opportunities AI presents for UX and user research
Integrating artificial intelligence into user experience design is a game-changer, bringing both exciting opportunities and unique challenges. AI can transform how we create and enhance digital products, but it’s important to fully understand its impact.
Enhancing user experience with AI powered tools
Artificial intelligence has the potential to significantly improve user experiences in several ways. Let’s see how:
1. Personalization: AI can analyze user data to provide personalized content and recommendations. For instance, streaming services like Netflix use specific algorithms but also AI to suggest shows and movies based on viewing history, creating a tailored user experience.
2. Automation: Repetitive tasks in the design process can be automated using AI, freeing up designers to focus on more creative aspects. This includes generating design elements, running usability tests, and even predicting user behavior, which is especially interesting.
3. Data analysis: AI excels at processing large amounts of data quickly. By analyzing user interactions and feedback, AI can identify patterns and insights that might be missed by human analysts. This helps in making data-driven design decisions that enhance usability and user satisfaction.

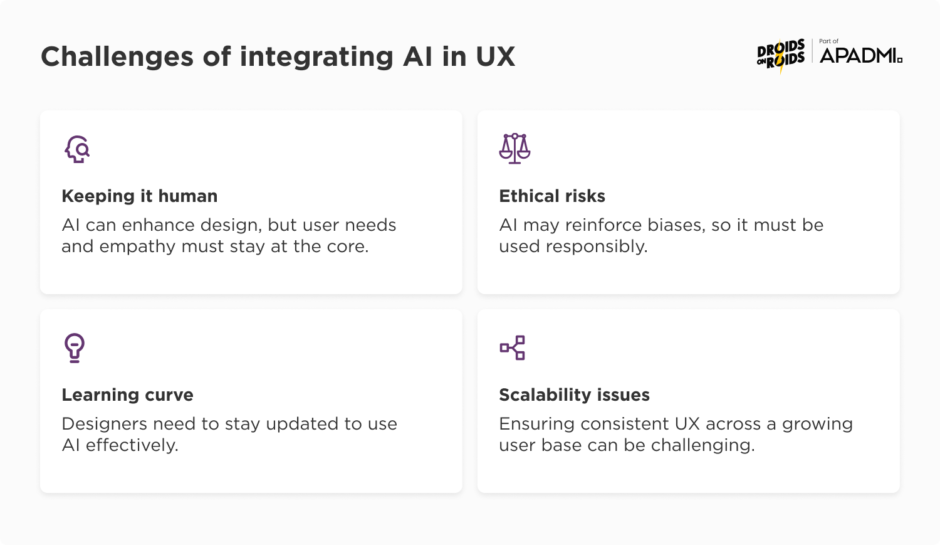
Challenges of integrating AI in UX
While the benefits are significant, there are also important challenges to consider:
1. Maintaining human-centric design: AI can provide valuable insights, but it’s essential to ensure that the design remains user-centered. “Human-centered” means that the design process prioritizes the needs, behaviors, and experiences of real users, ensuring that the end product is intuitive and meaningful for them.
This approach involves gathering user feedback and testing throughout the design process to create solutions that genuinely address users’ problems and enhance their overall experience. Over-reliance on AI might lead to designs that are efficient but lack the empathy and understanding that come from human insight.
2. Ethical considerations: AI systems can sometimes unintentionally reinforce biases present in the data they are trained on. UX designers must ensure that AI tools are used ethically and do not perpetuate harmful stereotypes or discrimination.
3. Complexity: Implementing AI in the design process can be complex and requires a certain level of expertise. UX designers need to continuously update their skills to effectively use AI tools – nowadays it’s very simple, and often doesn’t require financial investment. Some examples include:
- Listening to podcasts like Designing for AI to learn from experts.
- Joining live sessions to see how AI tools work in real-time.
- Subscribing to newsletters like UX Collective for the latest tips and trends.
- Taking courses on platforms like Interaction Design or Udemy.
4. Scalability: While AI-powered technologies enable UX designs to scale efficiently for large user bases, ensuring the quality of the user experience remains consistent across diverse users can be challenging. As the user base grows, maintaining personalization, avoiding bias, and ensuring data accuracy become increasingly difficult.
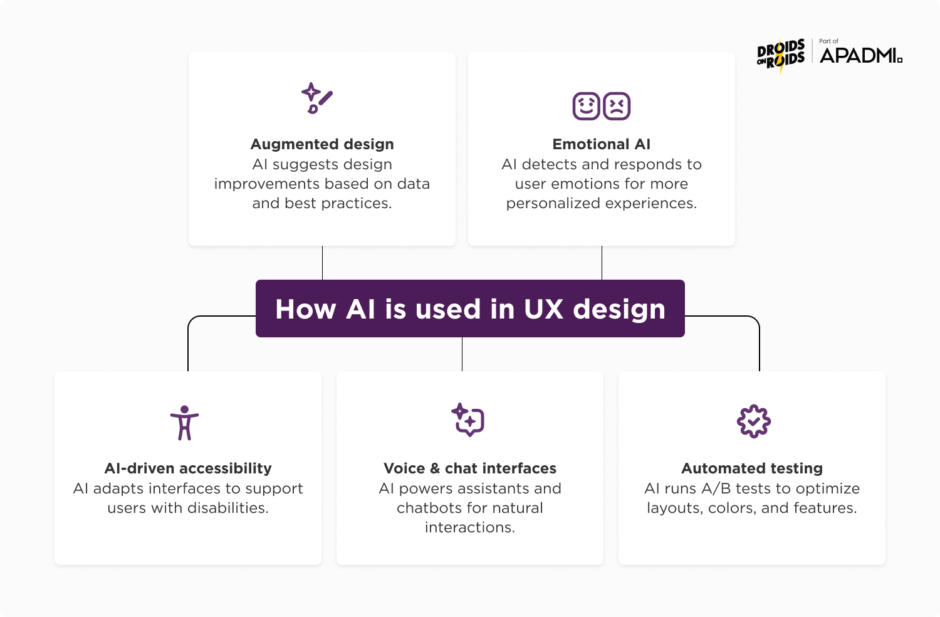
Practical applications of AI in UX design
We’ll explore real-world examples of how AI helps in different aspects of UX design. By understanding these applications and trends, you’ll see how AI can transform the design process, making it easier to meet users’ needs and improve overall satisfaction with digital products.
Looking ahead, the role of AI in UX design is expected to grow. Some emerging trends include:
Augmented design
Many AI tools that assist designers by suggesting design improvements or generating new design concepts based on user data and best practices. Such tools can suggest improvements to a design or even create new design ideas by analyzing user data and following best practices in design.
For example, if a designer is working on a website layout, AI might recommend better color schemes, layouts, or elements that would enhance the user experience based on what has worked well in similar projects. These AI tools help designers work faster and more effectively, freeing them to focus on creative decisions while the AI handles some of the more repetitive or technical aspects of the design process.
Emotional AI
There are also more and more systems being developed that can detect and respond to user emotions, creating more empathetic and responsive user experiences.
For instance, an AI powered app could detect if a user is feeling frustrated based on their tone of voice or facial expressions (in Poland, the Rossmann shopping app has a feature: when it detects a smile on your face, it gives you a discount in the store! So, shopping there literally pays to be happy!), and then offer help or adjust its responses to be more calming and supportive. This kind of AI aims to create experiences that feel more human and personalized, helping real users feel understood and improving their overall satisfaction with the product.
AI-driven accessibility
AI can help make digital products more accessible (accessibility refers to designing digital products that are usable by people of all abilities) to people with disabilities by automatically adapting interfaces to meet individual needs.
Let’s say a person with limited motor skills uses a smartphone to browse the web. AI could detect their difficulty in navigating small touch targets and automatically increase the size of buttons and links. Similarly, if the AI recognizes that the user has trouble reading small text, it could automatically switch to a higher contrast mode and larger font size, making the content easier to read. This kind of intelligent adaptation ensures that digital products are not just usable, but truly accessible to everyone, creating a more inclusive digital world.
Voice and conversational interfaces
AI powers voice-activated assistants and chatbots, making interactions with digital products more natural and intuitive. These interfaces can understand and process complex language inputs, letting users engage with products through simple, conversational commands.
One example of voice and conversational interfaces is the use of AI powered voice assistants, such as Apple’s Siri. This system enables users to interact with devices through voice commands, making it easier to perform tasks like setting reminders, controlling smart home devices, or searching for information, without needing to manually navigate through menus. In a UX design context, integrating such voice interfaces into web apps or websites can provide a more seamless and natural user experience, especially for users who prefer hands-free interaction.
Automated testing and optimization
AI can automate the process of testing different design elements to see what works best for real users. By running A/B tests and analyzing the results, AI helps designers optimize layouts, colors, and features more quickly and accurately.
Optimizely is an example of AI-driven automated testing and optimization. It enables designers to run A/B tests on different versions of a webpage to see which one performs better in terms of user engagement, click-through rates, or conversions. AI can automatically analyze the results of these tests and suggest the best-performing version. This reduces the time and effort required to manually analyze test results, allowing for quicker and more effective optimization of digital products.
Potential of AI
Integrating AI into UX design offers a promising future, with the potential to create more personalized, efficient, and user-friendly digital experiences. However, it is important to navigate these challenges thoughtfully, ensuring that AI complements rather than replaces the human touch.
By embracing both the opportunities and the challenges, we can use the full potential of AI to revolutionize user experience, leading to better products and happier users.
The role of UX research in AI development
UX research is essential in developing AI systems because it makes sure these technologies meet real user needs and improve the overall user experience. By studying how users behave, what they prefer, and how they emotionally connect with AI, researchers can help create designs that are easy to use and prove to be effective.
UX researchers set clear goals for their products and assess the pros and cons of different AI methods, always keeping the user’s experience in mind to make the AI feel comfortable and easy to use.
You may also like: AI in App Development: How to Improve Your Business
Understanding how people perceive AI, even if some effects are just in their minds (like the placebo effect), helps manage user expectations so that the AI performs as users hope it will.
UX researchers play a crucial role in developing AI-based products.
Here’s how our work typically looks:
- Setting clear product goals: A UX researcher, like me, starts by understanding the overall vision and objectives of the product. We collaborate with stakeholders, including product owners, developers, business analytics, success client managers, and UX and UI designers, to define what the AI system needs to achieve from the user’s perspective. This includes identifying key user needs, pain points, and desired outcomes.
- Assessing AI methods: Once the goals are set, UX researchers evaluate different AI approaches to determine which ones best align with the user’s needs and the product’s objectives. This might involve reviewing existing AI technologies, conducting user testing with prototypes, and analyzing data to see how different AI methods perform in real-world scenarios.
- Focusing on user experience: Throughout the process, UX researchers ensure that the user’s experience remains the top priority. They gather user feedback, conduct usability tests, and iterate on designs to ensure that the AI system is not only functional but also intuitive and comfortable for users to interact with. This might involve simplifying complex AI processes to make them more user-friendly or ensuring that the AI communicates its capabilities clearly to avoid confusion.
- Balancing pros and cons: UX researchers weigh the benefits and drawbacks of each AI approach, considering factors like ease of use, accuracy, and user trust. Their goal is to choose or refine AI methods that provide the best possible user experience, even if it means making trade-offs between technical capabilities and usability.
- Continuous improvement: After the product is launched, UX researchers continue to monitor user feedback and performance data to identify areas for improvement. They work closely with the development team to make adjustments that enhance the AI’s usability and effectiveness over time.
The impact of conversational interfaces on user experience and utility
Like I mentioned before, conversational interfaces, like chatbots, play a significant role in AI UX design by making user interactions both engaging and efficient. Users often prefer chatbots for private or sensitive tasks, such as purchasing embarrassing products, because they feel these AI tools are less likely to judge them than human agents, leading to a more comfortable user experience.
However, the human-like design of these AI-driven user interfaces can sometimes make it harder for users to get clear, actionable information, which complicates the UX process.
When chatbots proactively offer help, they can enhance user satisfaction, especially among older adults, by providing timely assistance and fostering a sense of companionship. But if these interactions aren’t well-timed, they can feel disruptive, highlighting a need for the careful consideration of UI components and visual design in UX projects.
Overall, while AI tools like chatbots can improve user experience, it’s important to balance AI-driven automation with human creativity in the design process to ensure these interfaces are effective and user-friendly.
Here are a few examples to help you understand the impact of conversational interfaces like chatbots on user experience:
- Private or sensitive tasks
A real user shopping for personal health products, like hair loss solutions, might prefer using a chatbot on a pharmacy website. The chatbot provides product recommendations and answers questions discreetly, without the user feeling judged or embarrassed, unlike a face-to-face interaction with a store assistant. - Challenges with human-like design
This refers to the creation of interfaces or systems, like chatbots, that mimic human behavior, appearance, or communication styles.A customer trying to resolve an issue with their internet service might interact with a highly anthropomorphic chatbot. While the chatbot uses friendly, human-like language, the user might find it frustrating when the chatbot can’t understand specific technical issues or provide detailed solutions, making the interaction feel less efficient. - Proactive assistance
An older adult using a health monitoring app might benefit from a chatbot that proactively checks in to remind them to take medication or log their daily exercise. This proactive assistance not only helps stay on track but also creates a sense of companionship, making the app more than just a tool but a supportive presence in a daily routine. - Potential disruptions
A user browsing a travel website might find it annoying if a chatbot pops up too frequently, offering help when they are not ready for it. For instance, if the chatbot interrupts the user while they’are comparing flight options, it could disrupt their focus, leading to a negative experience. This shows the importance of timing in chatbot interactions.
Understanding the impact of conversational interfaces, like chatbots, on user experience shows us how AI can make digital interactions more engaging and efficient. However, chatbots are just one piece of the puzzle. The real potential of AI in UX design goes far beyond this, as AI tools are now being integrated into various stages of the UX process to enhance how we create and refine user experiences.
The integration of AI tools to enhance UX work
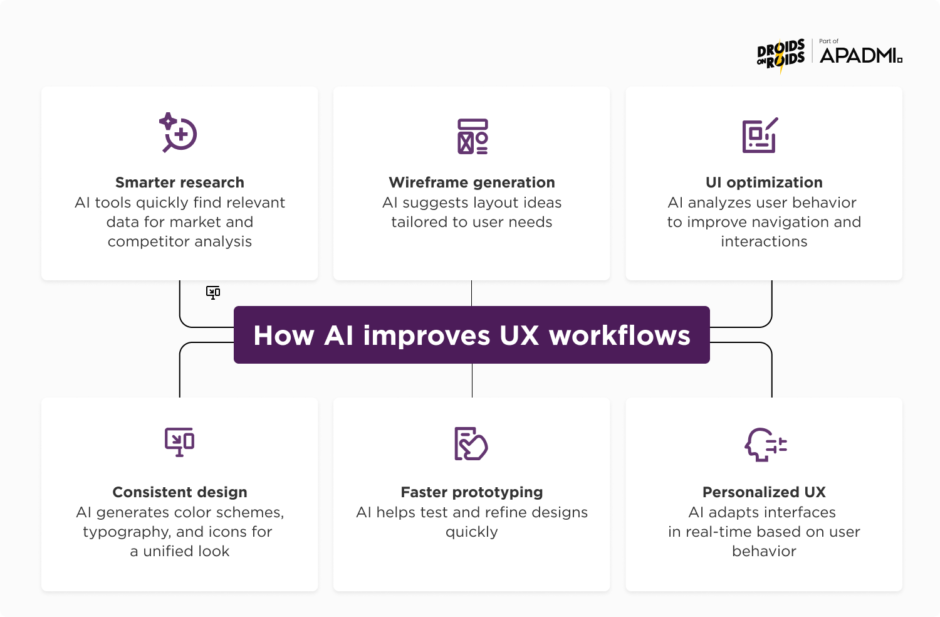
Adding AI tools into UX work is changing the way designers create and improve digital experiences. These tools help streamline the design process, making it faster and more efficient. By using AI, designers can generate ideas, create user-friendly interfaces, and optimize designs based on real user data.
Data research
Tools like ResearchRabbit make it quick and easy to find data and research articles that are useful for desk research, and even conduct the likes of competitor analysis, trend observation, or market research for a new app.
UX Rabbit lets users effortlessly search through a huge database of articles and studies by simply entering specific keywords related to your topic, providing relevant results very quickly. It helps to select the most important information related to your project, saving you from scrolling through numerous websites, which can be time-consuming.
Once you’ve gathered the information, you can use a tool like Scispace to extract the key insights and conclusions, making it even easier to compile and present your findings effectively.
It’s a tool that I use every day at work.
Wireframe creation and layout generation
In the early stages of a web app project, designers might use a UI generation platform powered by Generative AI to quickly produce various layout ideas. These AI tools can take a blank canvas and generate wireframes that align with industry insights and best practices.
For example, a designer could input a user persona and the AI would generate layouts tailored to the needs and preferences of the target users. This frees up designers to focus more on refining the design vision and strategy, rather than starting from scratch.
Optimizing user interfaces
Once a prototype is ready, AI tools can help optimize the user interface by analyzing how users interact with the design during usability testing. Advanced machine learning algorithms (machine learning is a type of technology that allows computers to learn from data and improve their performance on tasks over time without being explicitly programmed) can study user behavior, such as where they click, how long they stay on certain pages, and which elements they ignore.
Based on this data, the AI can suggest changes to the interface, such as moving a button to a more prominent position or simplifying a navigation menu, making the final product more intuitive and user-friendly.
UI design and consistency
During the UI design process, AI can assist in interface design by automatically generating key visual elements.
For instance, an AI tool could generate a cohesive color scheme, select appropriate typography, and create icons that match the overall design vision of the product. This helps maintain a consistent look and feel across the entire digital design. For example, in a web app, the AI ensures that all pages adhere to the same visual standards, which enhances the user experience and strengthens brand identity.
Prototyping and rapid iteration
In the prototyping phase, designers might use an AI-powered prototyping tool that enables rapid iteration. Such tools can quickly adapt to design changes, allowing designers to test different versions of the interface with real users.
The AI can also simulate various scenarios based on target user profiles, predicting how different groups might interact with the app. This not only speeds up the design process but also helps in refining the product to better meet user needs.
Advanced algorithms for personalization
In more advanced applications, AI tools using advanced algorithms can personalize the user interface based on real-time data.
For example, in a web app for online shopping, the AI could adjust the layout, recommend products, or even alter the color scheme depending on the user’s behavior and preferences. This personalized experience enhances usability and makes the app more engaging for each individual user.
Skills demanded of UX designers and researchers in the age of AI
We must be good at thinking critically and understanding emotions, as these skills help us use AI insights while keeping the focus on the user. Being able to use AI tools, like ChatGPT for generating ideas or Miro Assist for research, is also important. Both designers and researchers should understand data analysis and user behavior, as AI can make these tasks easier and help create more personalized experiences.
At Droid On Roids, we as designers and researchers are well-prepared and always ready to adapt to the growing use of AI in UX design. We constantly learn and improve our skills, keeping up with the latest trends and new technologies. By using AI tools, we can make interfaces better and create user experiences that are easy to use and tailored to the needs of real people.
We use AI to handle routine tasks, which frees us up to focus on more important aspects like thinking critically and understanding user feedback to make improvements. We’re dedicated to staying on top of innovation, ensuring that our projects not only meet but exceed our clients’ expectations.
If you want AI to be effectively integrated into the UX design of your next digital product, your team’s UX designers should focus on the following aspects:
Critical thinking
The critical thinking process involves sifting through the AI-generated insights to select the most relevant data that aligns with the project’s goals and deciding how to apply this information effectively in the design.
Imagine a scenario where a designer is working on a new mobile app for a health and wellness company. The designer uses Perplexity to gather insights about user preferences for health apps, including color schemes, navigation patterns, and content preferences. While the AI might generate hundreds of data points, the designer or researcher needs to critically evaluate which insights are worth using.
For instance, if the app targets young adults, insights about design preferences for older adults may be less relevant. The designer must then decide how to apply the relevant data to create an interface that resonates with the target audience.
Emotional intelligence
Understanding and empathizing with users is crucial, even when using AI. After generating visual concepts with Ideogram, which is an AI tool for creating custom typography and logo designs, a designer must assess whether the typography and logos evoke the intended emotional response from users.
For example, when designing for a children’s educational app, the designer should ensure that the AI-generated typography is playful and approachable, which requires an understanding of the emotional impact these visuals will have on young users.
Emotional intelligence also involves considering the broader emotional journey of the user as they interact with the product. A UX designer should anticipate how users will feel at different points in their journey and use AI tools to enhance positive emotions or mitigate negative ones.
For example, if a designer knows that users might feel frustrated during a complex task, they can use AI to suggest design elements that simplify the task, thereby improving the overall user experience.
Leveraging AI for creative exploration
Today’s Designers should be skilled in using AI tools like MidJourney for generating visual content. For instance, a UX designer might use it to create multiple mood boards or concept art during the early design phase. This enables the designer to explore different aesthetic directions quickly, facilitating creative brainstorming sessions and helping to visualize ideas more effectively before narrowing down on a specific design path.
What’s more, MidJourney can help in visualizing abstract concepts that might be difficult to convey through traditional design methods. For instance, if a project involves creating a futuristic user interface for a tech company, the designer can use MidJourney to generate speculative designs that push the boundaries of current UI conventions. This creative exploration is invaluable in the early stages of design, where the goal is to innovate and think outside the box, only afterwards focusing on to a specific design path.
Data analysis skills
Data analysis is a core competency for UX researchers and designers, especially when working with AI tools that generate or analyze large datasets. Understanding user behavior and being able to interpret data correctly is essential for making informed design decisions. A tool like Research Rabbit, which helps discover and organize academic research, can be very helpful in this process.
For instance, if a researcher is working on a project to improve the user experience of an online learning platform, they can use Research Rabbit to find relevant studies on e-learning user behavior, such as factors that enhance engagement or common pain points in the user journey.
By combining the insights gathered from Research Rabbit with analytics tools like Google Analytics, the researcher can identify patterns and trends that inform the design process. As an example, Google Analytics might reveal that users are dropping off at a particular point in the learning module. The researcher can then cross-reference this data with academic studies to hypothesize why this is happening. They can then suggest design changes to address the issue.
Ethical awareness
With the increasing use of AI in design, ethical awareness has become crucial as well. AI tools have the power to shape user experiences in many ways, and it is important to ensure that these tools are used responsibly.
For example, when using AI tools like Ideogram or MidJourney to generate logos, branding materials, or visual content, designers must be aware of bias (a tendency that affects impartial judgment, often leading to unfair or unbalanced outcomes in decision-making or behavior) or exclusion in the AI-generated outputs. AI models are trained on existing data, which can sometimes reflect societal biases. A designer must review AI-generated content critically to ensure that it does not reinforce stereotypes or exclude certain user groups.
Consider a scenario where a designer is creating a brand identity for a global company. If the AI-generated visuals reflect Western cultural aesthetics, the designer must recognize this bias and adjust the designs to be more inclusive, ensuring that the branding resonates with a diverse, global audience. This level of ethical awareness is crucial in creating designs that are not only effective but also inclusive.
Continuous learning
In a rapidly evolving world, to stay ahead, UX designers and researchers must commit to lifelong learning.
This can be achieved through various channels, such as subscribing to industry newsletters that provide updates on the latest AI developments, listening to podcasts that feature experts discussing new trends, and attending workshops or webinars to learn about new tools. Participating in online courses or certifications can also help professionals deepen their understanding of AI and its applications in UX design.
Additionally, joining professional communities and attending industry conferences lets UX professionals network with peers, share knowledge, and gain insights into how others are leveraging AI in their work. By consistently seeking out new information and experiences, UX designers and researchers can ensure they are always equipped with the latest tools and insights to excel in their work and adapt to the ever-changing landscape of AI in UX design.
Summary
AI is revolutionizing not only digital product development, but also product discovery and design. Having a team that effectively integrates AI into your project will help streamline workflows, optimize user experiences, and ensure efficient and successful product launches.
Here are a few of my final thoughts:
- AI speeds up UX design: By automating tasks like data analysis and UI optimization, AI reduces development time whilst maintaining high-quality standards.
- Personalization at scale: AI helps businesses to tailor experiences to individual users while scaling effortlessly.
- Human-centered design remains key: While AI provides valuable insights, maintaining empathy and human understanding in design is crucial. AI also helps business owners make more informed decisions about product direction and customer needs.
- Ethical awareness: Using AI responsibly ensures that biases are minimized and user trust is maintained.
- Ongoing learning: Stay updated with AI trends to continuously improve your digital products.
- Maximizing return on investment (ROI): By reducing manual tasks and increasing the accuracy of user insights, AI driven UX can help to maximize ROI.
At Droids On Roids, we keep up with new trends and use AI to optimize development and workflows where it makes sense. We’re always looking for ways to work smarter, but we approach AI with a healthy dose of realism – leveraging it where it adds value while keeping human expertise at the core. If you’d like to discuss how AI can be integrated into your product, feel free to reach out to us!